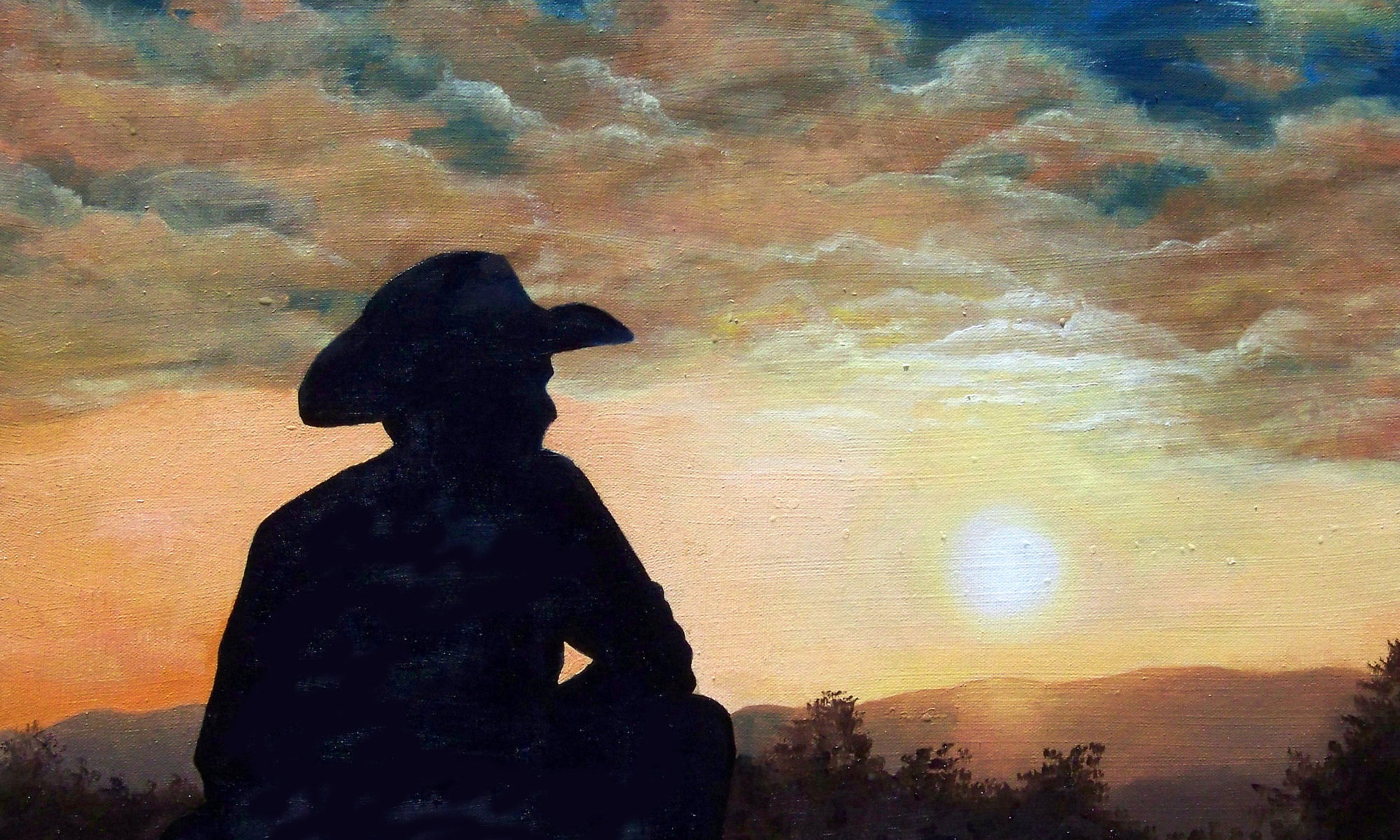
An art encyclopedia containing art-related words and their descriptions that begin with the letter “R”. Terms are listed in alphabetical order, from RABATMENT OF THE RECTANGLE to RYB. This reference includes over 20 art-related terms.
Quick links to more lists of art encyclopedia words are located at the end of the list.
Art Encyclopedia: “R” Words
Rabatment of the Rectangle
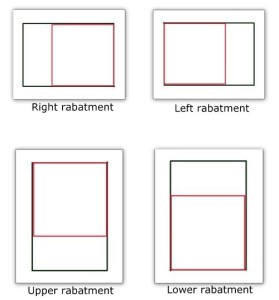
A compositional technique used for the arrangement of elements or to divide space within a rectangular frame to create a perfect square with four equal sides. It is found within any rectangle, with either a right or left rabatment for landscape (horizontal) rectangles and an upper or lower for portrait (vertical) rectangles. The most important aspects of a composition are placed within these squares, creating a center of interest. This technique enhances the visual appeal of compositions by ensuring the focal point is not directly in the center of the canvas.
Rabbet

In art, the “L” cut all around the perimeter of the frame, against which glass, mat, or picture panels are installed (see illustration).
Radial Balance
The balance as the result of components that are distributed around a center point or spring out from a central line.
Realism

A style of art most people consider to be “real art.” This is because it attempts to depict the topic as it appears in real life but stops short of appearing like a photograph. Realism is art without stylization or following the rules of formal artistic theory. Instead, the artist spends a fair amount of time and effort paying attention to creating an accurate depiction of life forms and objects, perspective, good composition, lights and darks, and color and tone.
Recycled Art

Contemporary works of art made from garbage, discarded items, or found objects that once had another purpose. Such items include plastic shopping bags, food containers, old plastic toys, vehicle tires, fabric scraps, bicycle parts, car parts, clothing, footwear, etc.
Red

One of the three primary colors of pigments used in painting, and the complement or opposite of the color green. In painting, red is used to create a multitude of colors when mixed with other hues.
Reference Photos
A collection of images used by visual artists for inspiration and composition. They can be of any living or inanimate object, place, animal, plant life, or individual. They are useful when it’s impossible for the artist to be there in person to physically observe the subject matter they want to paint or draw.
Reflected Light (in art)
The light that bounces off one object and strikes another. It adds depth and variation to an object, creating contrast in dark or uninteresting areas. Additionally, it can lighten some areas of the shadow, giving the shadows more depth and subtlety Understanding reflected light is essential for achieving a sense of three-dimensionality in artwork, whether drawing or painting. Also called bounced light or indirect light.
Relative Apparent Size
An optical illusion where distant objects appear smaller than those in the foreground due to our perception of depth and distance. When we observe a scene, our brain considers the relative sizes of items. If there are two objects that are the same size, the one closer to us will appear larger because it occupies more of our visual field. This phenomenon is crucial for artists to comprehend if they want to a create a sense of depth and spatial relationships in their compositions.
Relative Position
Refers to the position of objects relative to an imaginary line formed by our line of sight. We have a tendency to view items from our own eye level; objects in the foreground (or closest to us) appear on a lower plane, while distant objects appear on a higher plane. This is a notion that artists must understand if they wish to create a sense of depth and spatial relationships in their works.
Religious Art

Any form of artistic representation that uses religious inspiration to convey a message aimed at spiritual upliftment. It can be a sacred story or a profession of the artist’s faith, encompassing any set of individual beliefs, whether Christian or non-Christian. Also called “sacred art.”
Renaissance Art
The painting, sculpture, and decorative arts of the period of European history known as the Renaissance, an Italian term meaning ‘rebirth’. It originated in Italy around AD 1400 and is a significant period in European history that spanned about 200 years from 1400 to 1600. It reflects the cultural and intellectual changes in philosophy, literature, music, science, and technology. Renaissance art shifted from abstract forms of the medieval period to representational forms of the 15th century, featuring biblical scenes, portraits, classical themes, and contemporary events. Influenced by classical antiquity, Renaissance art focused on realism and the noble nature of humanity, reviving the classical art of Greek and Roman empires. The Renaissance period lasted until the 17th century, with works often capturing the beauty and complexity of the natural world. Famous Renaissance painters include Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael, known for their monumental works such as the Mona Lisa, the Sistine Chapel ceiling, and the School of Athens.
Rendering
An important process in art that involves creating a realistic representation of a figure, object, or scene using a variety of methods. In conventional art, rendering entails painting with lines, shapes, and colors, whereas in digital art, it entails finishing a piece with computer effects. This step entails working on lighting, shading, and adding details and textures. In both conventional and digital art, rendering improves the quality of a drawing by making it more visually appealing. Shading, lighting effects, and simulated shadow/reflection are among the techniques used. Finally, rendering adds depth and reality to the artwork, making it a useful tool in the art industry.
Repetition
A design principle that involves the repetition of an element or a series of similar elements, either regularly or irregularly.
Representational Art
Also called figurative art, an artwork that represents objects or events in the real world. It is an art that is clearly identifiable as something that already exists in life. The term is in contrast to abstract art.
Reproduction
A copy of an original print or fine art piece. The reproduction could be in the form of an offset-lithographic print or even reproduced using the same medium as the original.
Retreating Colors
Cool colors like blues, greens, and purples appear to recede into the background, creating a sense of distance. Retreating colors are opposite of “advancing colors.”
RGB
An acronym that stands for Red, Green, and Blue. RGB is a color model used to specify colors in digital images and computer graphics. It uses three numbers, each representing 8 bits with integer values ranging from 0 to 2552, to indicate the intensity of the red, green, and blue colors.
Rhythm
A continuance, a flow, or a feeling of movement achieved by the repetition of regulated visual units.
Rich Black

A printing term referring to a black ink mixture that has a percentage of cyan, magenta, and yellow added to the black. Plain black is 100% black ink and often appears dull and lacks a certain depth. Whereas rich black results in a darker, richer tone of black. The mixture is often 60% cyan, 40% magenta, 40% yellow, and 100% black, although the percentage can vary.
Right Brain
Refers to a theory in which the right side of the brain is the creative side, responsible for art and spatial comprehension. In contrast, the left side is responsible for reading, verbal, and mathematical sorts of tasks.
Round Art Brush

A traditional brush shape with a round or pointed tip in a round ferrule. The long hairs have large bellies and taper at the ends. They are ideal for sketching, outlining, detailed work, controlled washes, and filling small areas. Use one to create thin to thick lines that widen as you press down. This brush can hold a lot of paint for thick, large, and bold strokes. Thin, delicate marks are also possible if the pant loaded to the belly is thin. Rounds are most often used for small details and line work.
Rule of Odds
A principle of composition that states an image with an odd number of elements is more captivating than an image with an even number, since an even number of elements will create symmetries that can quickly become boring.
Rule of Space (in art)
A technique that creates a sense of motion or activity in a composition by creating a negative space relating to the focal point. For example:
-
- When painting a portrait, if your subject is not looking directly at you, leave some negative space in the direction the eyes are looking, even if they are looking at something off-canvas.
- When picturing a moving object, such as a runner or vehicle, placing negative space in front of the runner or object rather than behind creates a sense of direction or the implication of an eventual destination.
- If your subject is pointing at something or aiming at an object, place some negative space where the subject is pointing or aiming.
Rule of Thirds

A strategy used by professional photographers to aid them when composing the subject matter of their photographs. Painters can use this efficient technique as well. It involves dividing the painting surface into nine equal parts and the key elements needed in the composition are then positioned along these lines or intersecting points.
Using the rule of thirds ensures that a painter will never have a composition that visually split’s the painting in half (vertically or horizontally). Nor will they have one with the main focus right in the center, creating a bull’s-eye and thus leaving the rest of the painting to be ignored. Instead, the eye is drawn to the focal point and then around the artwork, generating a flow from one element to the next.
RYB
Stands for Red, Yellow, Blue. The primary colors used in painting and art. Also, see Primary Colors.
You May Also Like
This art encyclopedia is provided as a valuable resource for art enthusiasts. If you like the information here and find it helpful, please consider purchasing a painting. Your support helps to cover the cost of keeping this art encyclopedia online. Simply click or tap the thumbnail link of any Teresa Bernard oil painting to view additional details.

12″ w x 16″ h

(2023)
12″ w x 9″ h

(2021)
12″ w x 9″ h
Art Glossary Quick Links
Contributing to The Art Dictionary
The art encyclopedia is a work in progress. New terms and definitions are added on a regular basis. If you know of an art term and definition that isn’t already listed in it, but you believe it should be, send it to us and we’ll consider adding it. We’ll let you know if we do. Thanks!
Thanks for reading this!