VALUE | VOLUME
Quick links to more art terms and definitions are located at the end of the list.
Value
The degree of lightness or darkness of any given color. Value is defined by the color’s proximity to white. For instance, lighter colors such as yellow will have lighter values than darker colors like navy blue. Adding white or black to a hue changes its value.
A good way to see the difference in color values is to look at the greyscale below. White is the lightest value, while black is the darkest. Middle gray is the value halfway between these two extremes.
![]()
Adding white to a color creates a “tint” making its value lighter. When you add black to a color, its value darkens, resulting in a “shade” of that color.
![]()
Value Contrast (in art)
Refers to the difference between light and dark. It is based on the relative lightness or darkness of a color, regardless of hue. It plays a crucial role in creating depth, three-dimensionality, and visual interest. Value contrast can be used to make an object appear closer or further away, as well as to convey drama or movement.
Value Relativity (in art)
Refers to the juxtaposition of different values (lightness or darkness) next to each other within an artwork. Essentially, it’s the deliberate arrangement of contrasting values to create visual impact and enhance the perception of form, depth, and space.
Value relativity isn’t just about individual shades; it’s about how those shades interact with one another. By skillfully orchestrating these interactions, artists breathe life into their compositions, inviting viewers to explore the interplay of light and form.
Value Scale
In the art world, a value scale is an essential tool for artists. It assists in organizing and comprehending tonal values by representing them on a grayscale. For information on how to create a value scale, click the link.
Vanishing Point
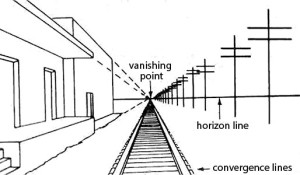
(Also known as “a point of convergence.”)
In perspective, the point on the horizon line where all parallel lines appear to recede and converge; it’s the point where visibility ends.
The vanishing point is a key element in creating the illusion of depth and three-dimensionality in drawings, paintings, and photographs. Essentially, it’s what allows artists to make their two-dimensional works look three-dimensional.
Vanitas Still Life

(A Latin term meaning “vanity.”)
A style of still life painting made popular in the Netherlands during the 16th and 17th centuries. Compositions include objects or symbols of mortality to remind people that life is fleeting, and material things and worldly pleasures are temporary. A typical vanitas still life is characterized by and may contain symbolic images like skulls, extinguished candles, rotting fruit, bubbles, smoke, watches, hourglasses, musical instruments, wine, and books.
Variety (in art)
Refers to the use of different elements, techniques, and design to create visual interest and intrigue. It prevents an artwork from becoming monotonous and boring and is essential for maintaining a rich visual experience. The principle of variety in art involves the use of different forms, textures, colors, and other elements to create interest and contrast. By incorporating a variety of shapes, textures, colors, and other elements, art becomes more dynamic and eye-catching, attracting viewers and enhancing the overall quality of the artwork.
Varnish
A transparent hard, protective coating or applied to paintings to seal and protect the surface, creating a barrier against moisture, dust, and pollutants. Varnish also acts to intensify the appearance of the colors on the painting surface making them look more saturated. For more information on this topic see blog article “The Importance of Varnishing Oil Paintings.”
Vector Graphic
A graphic made up of mathematically defined curves and line segments called vectors. Vector graphics are editable through the manipulation of their lines and segments, allowing for the resizing and repositioning of the entire image. They can be scaled up or down without any degradation in resolution, maintaining clarity at any size.
Veduta
(Italian for “view”; pl: vedute.)
Refers to a highly detailed, typically large-scale painting, drawing, or etching that portrays a cityscape, township, or other urban scene. These pieces of art offer accurate depictions of urban landscapes, skillfully capturing streets, buildings, and other details, as well as the overall ambiance of a location. See also “Urban Landscape.”
Vedutisti
Refers to a specific group of artists who specialized in creating “vedute”—highly detailed and often large-scale paintings or prints of cityscapes and other vistas. See “veduta.”
Vegetable Still Life

A type of still life that focuses on the beauty and variety of vegetables, often highlighting their textures, colors, and forms. Vegetable still lifes can evoke a sense of simplicity and natural beauty, often emphasizing the freshness and organic qualities of the produce. This style has been popular among artists who enjoy capturing the intricate details and vibrant colors of vegetables.
Vermilion

A scarlet red pigment of variable color that is vivid red but sometimes with an orange tinge. Initially, the vermilion pigment was made from a highly toxic mineral called cinnabar, which contains mercury. However, a synthetic pigment called cadmium red was developed to replace vermilion because of the toxicity of mercury.
Vertical Balance
Refers to a specific type of balance where the visual weight within an artwork is evenly distributed along a vertical axis. Imagine slicing an artwork vertically down the middle: the elements on one side should mirror or balance out the elements on the other side.
Victorian Classicism
Refers to a specific artistic style prevalent during the reign of Queen Victoria (1837–1901) in the United Kingdom. Artists following Victorian Classicism adhered to strict academic rules and compositional guidelines. They looked to the British and European Art Academies for inspiration. Their color choices were restrained, favoring a more subdued range of hues. Victorian Classicism blended tradition, moral purpose, and visual aesthetics. It captured an era of societal shifts, technological advancements, and artistic exploration.
Video Art
A genre of art involving moving imagery and audio-visual technology to produce videotapes for viewing on a television screen. This form of art gained rapid popularity in the ’60s and ’70s with the widespread availability of inexpensive videotape recorders.
Viewfinder

A tool used to look through to compose an image. This tool helps select the most interesting composition to be found in a larger image by cropping out unwanted perimeters. In photography, a viewfinder is what the photographer looks through to compose, and in many cases to focus, the picture (see illustration). For more information, see the article titled Making and Using a Viewfinder to Compose Better Paintings.
Vignette
In the realm of art and design, a vignette refers to a unique framing form applied to an image or painting where the borders are undefined and seem to fade away gradually until it blends into the background. The beauty of a vignette lies in its ability to guide the viewer’s eye, emphasize the central content, and incorporate negative spaces (such as corners) into the overall design.
Viking Art
(Also called Norse art.)
An art form that flourished during the Viking Age (8th to 11th centuries CE) and was created by Scandinavian Norsemen. Viking art, which consists primarily of objects, shares design characteristics with Celtic, Germanic, Romanesque, and Eastern European traditions. Current knowledge of Viking art is primarily based on archaeological discoveries such as jewelry, weapons, and runestones.
Violet

A secondary color formed by mixing the primary colors red and blue. See “Secondary Colors.” The complement or opposite of the color yellow. The color of violet is named for the violet flower from which the color is derived.
Viridian

A darker blue-green pigment composed of more green than blue falling between teal and green on the color wheel. Viridian takes its name from the Latin Viridis, meaning “green.”
Visionary Art
Art that transcends what lies beyond the boundary of the physical and scientific world to portray a broader vision of awareness, including themes of spiritual, mystical, or inner awareness as seen or experienced in the images of dreams or trances.
Visual Art
A form of artwork, such as graphic design, painting, drawing, photography, printmaking, ceramics, crafts, or sculpture, created primarily for visual perception and exists in permanent form.
Visual Artist
In the realm of art and design, a visual artist is a creative professional who expresses concepts and emotions through various forms of visual art. These forms include painting, drawing, photography, sculpture, and graphic design. Visual artists may work in fields such as contemporary art, illustration, advertising, or multimedia. Their primary goal is to create unique and original works that reflect their artistic vision while effectively communicating messages to their audience.
Visual Communication
The communication of ideas through the graphical display of information. Primarily associated with two-dimensional images, it includes alphanumeric, art, signs, and electronic resources. Recent research in the field has focused on web design and graphically oriented usability.
Visual Economy (in art)
(Also called Simplicity.)
The removal of all non-essential or unimportant elements and details that do not contribute to the essence of the overall composition. Its purpose is to allow what is most important to be the main focal point. The concept of simplicity is that a good composition is the most simple or straightforward solution to the design problem.
Visual Texture

Refers to the perceived smoothness and flatness of surfaces in photographs and paintings. Artists create the illusion of texture by using elements like line, shading, and color to create patterns. These textures are created by repeating lines, dots, or shapes, and can be varied in size, density, and orientation to achieve desired effects. Despite how rough objects may seem to appear in a picture, the image’s surface is always going to be smooth and flat to the touch.
Visual Weight
An important concept in the realm of art and design, visual weight refers to the amount of attention a specific element or area in a composition attracts to itself. Contrast, color, size, and shape all have an effect on visual weight because it affects the balance and harmony of an image making some elements may appear heavier or lighter than others. Thus, visual weight is essential for achieving balance, harmony, and visual hierarchy in artistic works.
Visualization Design
A process that aims to make information more understandable and visually appealing by converting complex ideas into simpler representations. Visualization design bridges the gap between quantitative and qualitative data through visual means, transforming data into compelling visuals like charts and diagrams.
This process involves carefully selecting images, typography, spacing, layout, and color to improve the design’s aesthetic appeal and usefulness. Key aspects of visualization design include charts, graphs, histograms, maps, plots, timelines, tables, word clouds, diagrams, and matrices. Effective data visualization improves communication and decision-making, going beyond aesthetics to optimize user experience and conversion.
Volume
In the context of three-dimensional geometry, volume refers to the amount of space occupied by an object. When we discuss volume, we’re essentially measuring the capacity of that object—the three-dimensional “room” it fills.
You May Also Like
This art terms wordlist is provided as a valuable resource for art enthusiasts. If you like the information here and find it helpful, please consider purchasing a painting. Your support helps to cover the cost of keeping this art thesaurus online. Simply click or tap the thumbnail link of any Teresa Bernard oil painting to view additional details.

(2011)
20″ w x 24″ h

(2023)
12″ w x 9″ h
Art Glossary Quick Links
Contributing to The Art Dictionary
The art terms wordlist is a work in progress. New terms and definitions are added on a regular basis. If you know of an art term and definition that isn’t already listed in it but you believe it should be, send it to us and we’ll consider adding it. We’ll let you know if we do. Thanks!
Thanks for reading this!