DADA | DYNAMIC COMPOSITION
Quick links to more art terms and definitions are located at the end of the list.
Dada
An avant-garde art movement that emerged during World War I in Europe in negative reaction to the atrocities and folly of war. Dada artists poked fun at all the established traditions and tastes in art with works that were deliberately satirical and nonsensical.
DayGlo Colors
Also called fluorescent colors and neon colors, are bright, clean materials with a unique “glowing” effect under ultraviolet or black light. They are widely used to attract attention, focus attention on objects, warn people of hazardous situations, and get an object or situation noticed. You commonly see them in traffic cones, detergent packaging, tennis balls, and fishing lures. They appear in various media, including oil and acrylic paints, inks, dyes, markers, and crayons. See also, “fluorescent colors.”
Dead Color Layer
A crucial stage in painting, consisting of a monochrome underpainting as the base layer before additional layers of paint are applied to create depth and vibrancy. This stage establishes the composition, as well as main light and dark relationships in the final artwork. Also referred to as the monochrome version of the final painting.
Decalcomania
An art technique involving the transfer of images from one surface to another. This method dates back to the 18th century and is often used in ceramics, pottery, and glasswork. The process typically involves pressing a paper with a printed design onto a substrate such as ceramic or glass, then removing the paper to leave the image on the surface.
In the 20th century, surrealist artists like Max Ernst adapted decalcomania as a painting technique, using it to create intricate, abstract textures and patterns. This involved spreading paint between two surfaces and then peeling them apart to produce unique effects.
Decalcomania’s versatility and capacity for creating unexpected results make it a fascinating technique in both decorative and fine arts.
Decorative Art
A form of visual art that involves the design and decoration of objects that have both aesthetic and practical value. Ceramics, jewelry, enamels, furniture, glass, ivory, metals, and textiles are examples of decorative art forms, particularly when utilized as interior decoration.
Decoupage
(A French word meaning “to cut out.”)
The art of decorating objects by gluing colored paper cutouts onto them, often combined with special paint effects, gold leaf, and other decorative elements. This technique can be applied to various surfaces like wood, metal, or glass, and involves sealing the layers with varnish to create a smooth, polished finish.
Design (in art)
Refers to the thoughtful arrangement and organization of visual elements like line, shape, texture, color, form, and space. It involves applying principles such as balance, emphasis, contrast, and movement to create visually appealing and meaningful compositions. Design serves as the underlying structure that guides the viewer’s experience and helps convey the artist’s intended message or emotion. It’s used in various art forms, from graphic design and illustration to interior design and fashion.
Designer
A designer is a person who plans the appearance and function of a product, structure, or system before it’s made. They work in various disciplines like graphic design, web design, game design, interior design, fashion design, architecture, and industrial design. Designers communicate ideas through visual representations and use design tools like digital design and sketches to create artwork.
Designing
The process of creating a plan or blueprint for a work of art. This involves conceptualizing and organizing elements such as lines, shapes, colors, textures, and space to achieve a specific aesthetic or functional goal. The design process can be applied to various forms of art, including graphic design, fashion design, interior design, and more. Designing often starts with brainstorming and sketching ideas, followed by refining and developing these concepts into a final piece. It requires both creativity and technical skills to balance visual appeal with practical considerations.
Digital Art
Refers to any artistic work or practice that uses digital technology as an essential part of the creative or presentation process. This broad category includes various forms such as digital paintings, illustrations, 3D models, animations, and even interactive installations. Digital art can be created using software like Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, or specialized 3D modeling programs. Artists might use a graphics tablet, a computer mouse, or even a smartphone to create their work. The flexibility and accessibility of digital tools allow for endless creative possibilities, making it a popular medium for both professional and amateur artists.
Diorama
A three-dimensional miniature model representing a scene, typically depicting historical events, natural environments, or fictional scenes. These models often include detailed figures, landscapes, and objects arranged to create a realistic and immersive experience.
Dioramas are commonly used in museums to provide educational displays, helping to visually convey complex subjects or moments in history. They can range from small, tabletop-sized models to large, room-sized installations. The meticulous attention to detail and scale in dioramas makes them a powerful tool for storytelling and education.
Diptych
(Pronounced dip-tik. From the Greek words “di” meaning “two,” and “ptychē” meaning “fold” or “layer.”)
A work of art consisting of two painted or carved panels where each panel depicts a different but related scene. The two panels in a diptych work in harmony to create a single cohesive art piece. These panels can be hinged together or presented side-by-side. Diptychs aren’t limited to any specific medium. They can be paintings, drawings, carvings, or even photographs. See also Polyptych.
Distemper (in art)
A traditional painting technique that employs water-based paint mixed with a binder, such as animal glue or casein, to create a matte finish. This method was widely used in the past for both fine art and decorative purposes, particularly before the advent of oil paints. Distemper is valued for its ease of application and the soft, velvety appearance it imparts to surfaces. However, it is less durable than oil paint, making it more suitable for works intended for indoor display or temporary projects.
Doodle
A drawing created while a person’s attention is otherwise occupied. Doodles are simple sketches that may hold specific representational significance or be merely a collection of arbitrary and abstract strokes.
Doodling
The act of drawing or sketching aimlessly, often without a specific goal or finished product in mind. It typically involves creating simple, unstructured drawings, such as patterns, shapes, or even recognizable figures, usually done while the mind is otherwise preoccupied. Doodling can be a great way to relax and enhance creativity. It helps improve concentration and can even aid in processing information during activities like meetings or lectures. Despite its casual nature, doodling is considered a form of art because it allows for self-expression and creativity.
Double Loading
A painting technique that involves loading a brush with two colors side by side. This is a technique typical of tole and other kinds of decorative painting. Also known as “sideloading.”
DPI
(An acronym that stands for “dots per inch.”)
A measure of dot density that refers to the number of individual dots in a line across a 1-inch span. Higher DPI values result in better print quality and sharper images, affecting image clarity and detail. It characterizes the resolution of hard copy prints and digital prints.
Draftsmanship
Refers to the skill and technique involved in drawing. This encompasses a wide range of abilities, from creating precise technical drawings and architectural plans to expressive, freehand sketches. A draftsman, or draughtsman, is an artist who demonstrates a high level of proficiency in drawing, often characterized by their control over line quality, perspective, anatomy, shading, and composition.
Draftsmanship is fundamental to many forms of art and design, serving as the basis for painting, sculpture, illustration, and more. Mastery of this skill allows artists to accurately capture the visual world and effectively communicate their ideas.
Drawing
The art or technique of producing images on a surface, typically paper, by making marks with tools like ink, graphite, chalk, charcoal, or crayon. It involves creating lines and areas of tone to represent objects, concepts, emotions, or abstract forms. Drawing is fundamental to many visual arts, serving as a basis for painting, sculpture, and other forms. It can range from simple sketches to highly detailed works and is often used for planning and conceptualizing larger projects.
Drip Painting
An abstract art style that gained popularity in the 20th century through the work of Jackson Pollock. This technique involves dripping or pouring paint onto the canvas, highlighting movement and spontaneity to create dynamic and unique effects.
Drypoint
A printmaking technique where an image is incised into a plate with a hard-pointed needle or similar sharp tool. The plate is usually made of metal, such as copper or zinc, but it can also be plastic or acrylic. Unlike etching, drypoint does not involve the use of acid to create the image.
The process of drypoint involves scratching the design directly onto the plate, creating a burr (a raised edge) along the incised lines. When ink is applied to the plate, the burr holds the ink and produces rich, velvety lines with a distinctive character. This quality makes drypoint particularly valued for its expressive potential and tactile effects.
Duotone
A printing technique that uses two colors to create a tonal image. This method involves printing an image with two different inks, typically a dark color and a lighter one, to produce a richer and more dynamic effect compared to a standard monochrome image.
Duotones can create striking visual contrasts and a sense of depth, making them a popular choice for creative and impactful imagery.
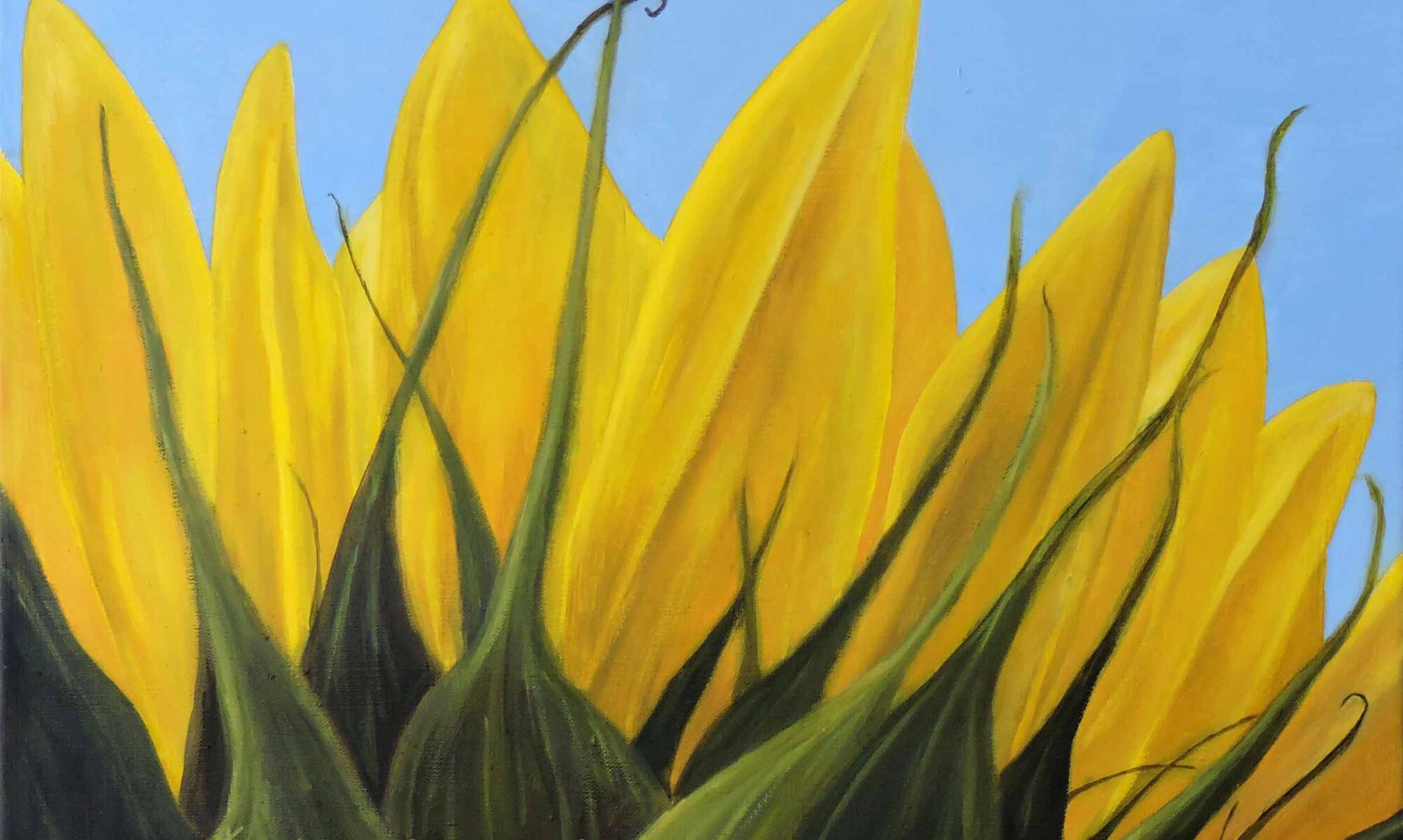
Dynamic Composition
Refers to the arrangement of elements in a visual work that creates a sense of movement, energy, and tension. This type of composition actively guides the viewer’s eye throughout the piece, often using diagonal lines, strong contrasts, and asymmetrical arrangements to evoke a sense of vitality and action.
In dynamic compositions, elements are placed in a way that disrupts balance and symmetry, creating visual interest and engagement. Techniques such as overlapping forms, varied scales, and directional lines contribute to this lively effect. Artists use dynamic composition to bring life and excitement to their work, enhancing the emotional impact and narrative flow.
You May Also Like
This dictionary of art terms is provided as a valuable resource for art enthusiasts. If you like the information here and find it helpful, please consider purchasing a painting. Your support helps to cover the cost of keeping this art terminology lexicon online. Simply click or tap the thumbnail link of any Teresa Bernard oil painting to view additional details.

6″ w x 6″ h

(2019)
6″ w x 6″ h
Art Glossary Quick Links
Contributing to The Art Dictionary
The art terms dictionary is a work in progress. New terms and definitions are added on a regular basis. If you know of an art term and definition that isn’t already listed in it but you believe it should be, send it to us and we’ll consider adding it. We’ll let you know if we do. Thanks!
Thanks for reading this!